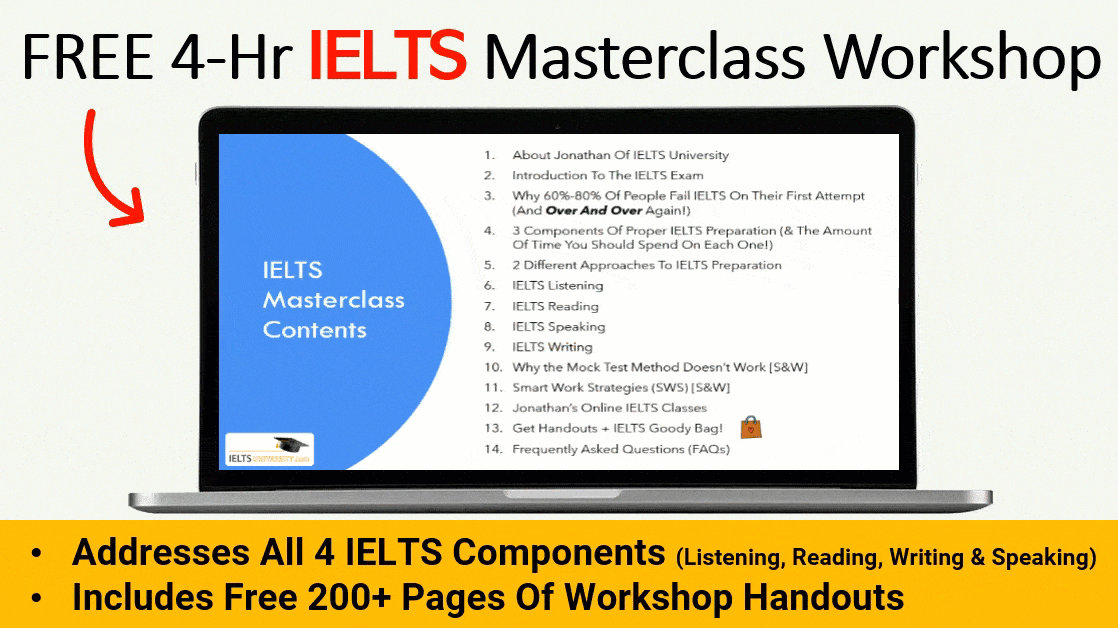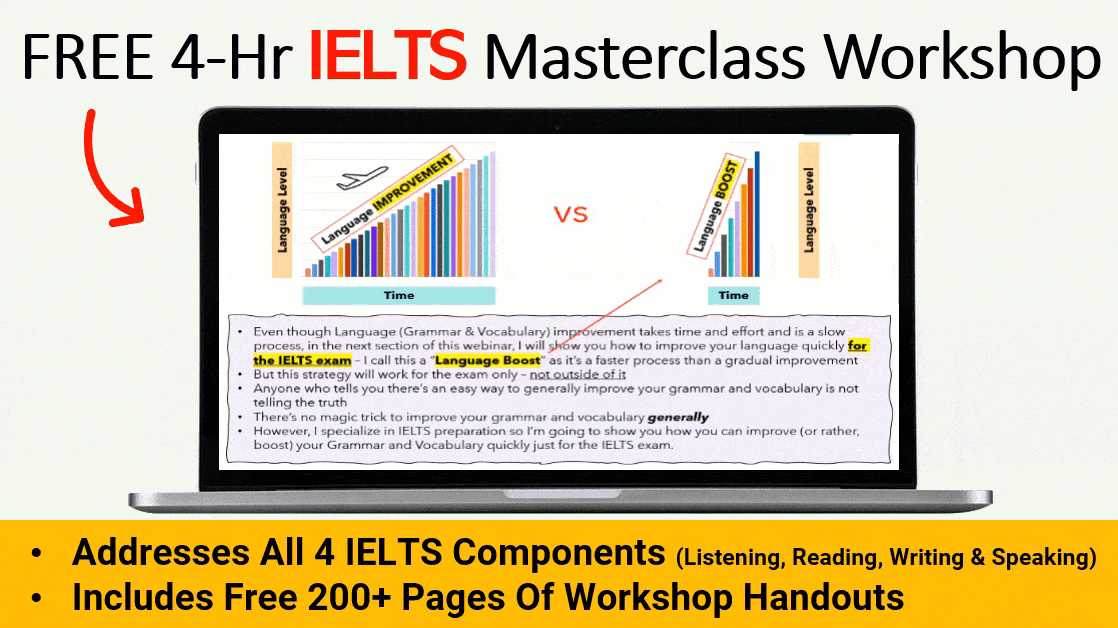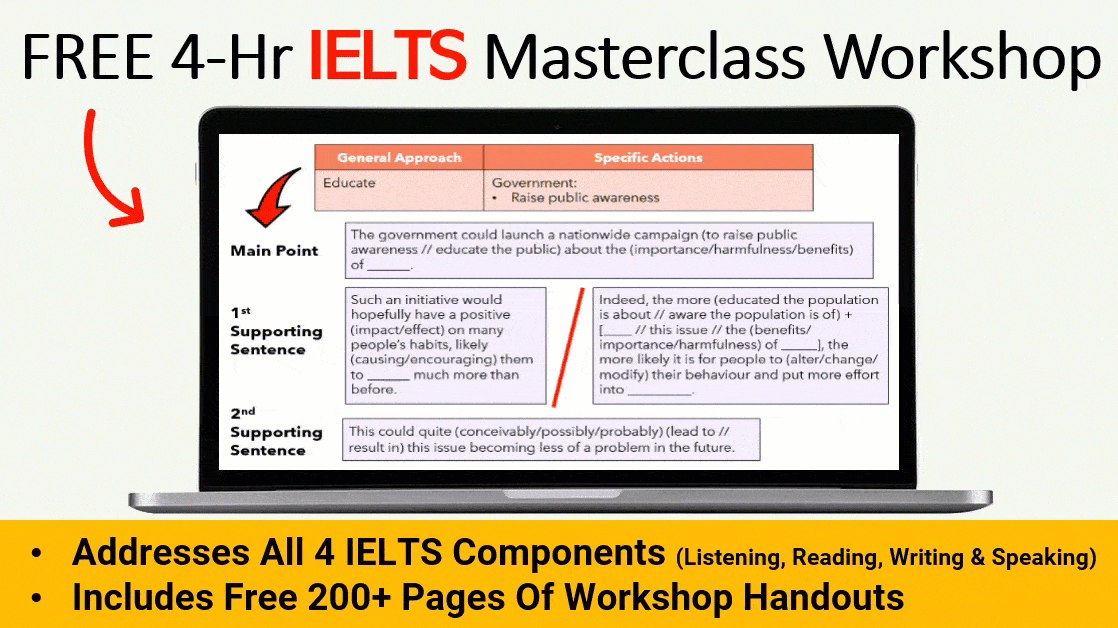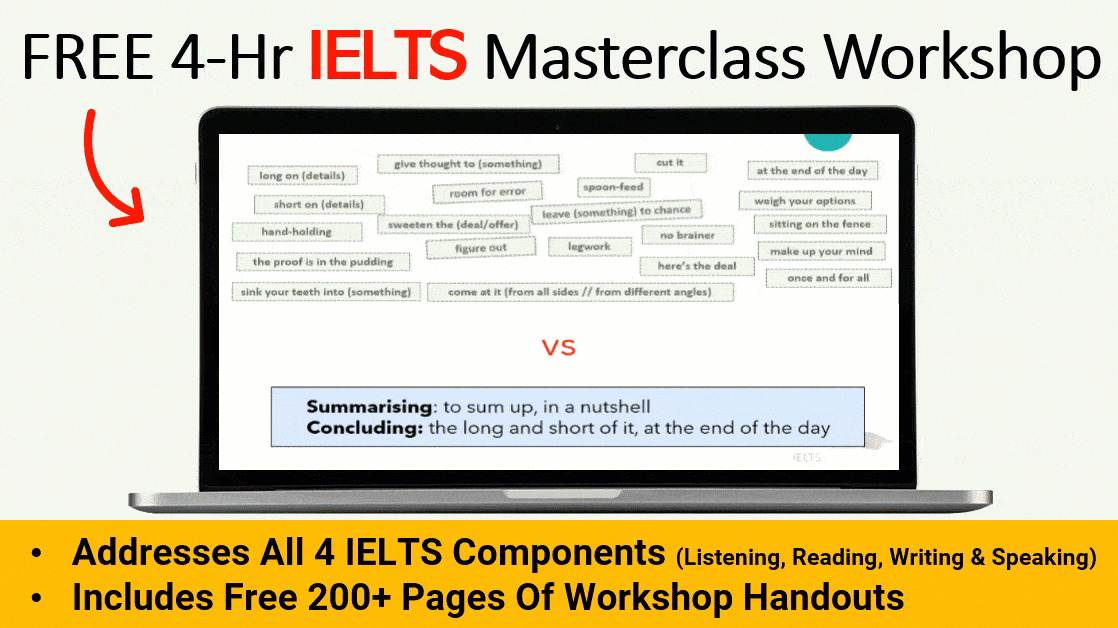
The IELTS reading test is used to assess a student’s ability to comprehend the information given in reading passages that relate to educational or life skill situations
There are around 12 different types of questions that are found within the test and solving each of them requires a unique strategy. In this article, we will discuss each of these questions types as well as a few strategies and tips that are necessary to solve them.
The IELTS reading question types include:
- Multiple-choice questions
- Matching Headings
- Matching Features
- Matching Information
- Matching Sentence Endings
- True/False/Not Given questions and Yes/No/Not Given questions
- Summary, Table, Note, Flowchart Completion
- Diagram Labelling
Matching Headings
This question requires choosing headings that match the gist of the given paragraphs. (basically, each heading summarizes a paragraph within the text). Before you actually look at the question you should first skim through the text for a general understanding of the text. Once this is done, you can look at the headings. The headings always match the main ideas of a paragraph, but they are paraphrased meaning that they may not contain the same words as the passage but them.
There are usually more headings than actual paragraphs which means that sometimes more than one heading seems to match a paragraph. This is because Some of the headings are distracters, having a similar meaning to the actual answer.
Sample Question:
Short Answer Questions And Completion Tasks
Completion tasks include the following type of questions
- Note Completion
- Table Completion
- Summary Completion
- Flow Chart Completion
They are all quite similar. In these types of questions, one has to fill in the blanks that are related to either of three things.
- A paraphrased sentence relating to the passage
- A flow chart
- A table
- A question with a short fixed answer
For these questions, you will be asked to provide specific information in the form of words and/or numbers. For this type of question, it is especially important to read the instructions carefully. The word limit is important. If you answer with more than the required number of words, your answer will be marked as incorrect. For example, if the instructions say to ‘answer with one word only’ and you answer correctly with two words, your answer is still considered incorrect. This is also true for words that are incorrectly spelt. Make sure that you copy answers from the text carefully, without changing the word in any way. If the answer does not fit grammatically, exactly as it is, you probably have the wrong answer.
Sample Question:
Matching Endings
This a question type in which we are given incomplete sentences along with options for suitable endings. Both the sentence beginning and ending options are paraphrased, meaning that they will not appear in exactly the same way in the text.
In this question there are usually more options than sentences and these incorrect options are meant simply to confuse students. These options are often worded very similarly to the text with a few minor differences. When you do that match an ending to a sentence beginning, make sure that the resulting sentence should be grammatically correct.
Sample Question:
True/False/Not Given:
This is a question type which asks you to decide if certain statements/facts agree with the text or not (true/ false) or if they are altogether not mentioned in the text at all (not given).
Before I explain further, we first need to clarify what “true, false and not given” actually mean in terms of this question type.
- True – means that the statement is a fact that is clearly mentioned in the passage even if it is paraphrased.
- False – means that the opposite of the statement is present in the passage.
- Not Given – a statement can be considered as “not given” only when both the statement and its opposite is not mentioned in the text. This option can be particularly tricky as sometimes only part of the statement is mentioned along with some key differences in wording. For example, all vs. some or most vs. a few
For this question, it is important to avoid using your own personal opinions to answer. In some instances, you may know of something to be true but if it is not mentioned in the text you have to answer it is not given.
Multiple Choice Questions
These are questions in which you are asked to choose the correct option for statement endings or answers to questions based on the text. There are different types of multiple-choice questions namely:
- Questions with only one correct option out of four options.
- Questions where it is required to choose more than one option from a number of options greater than four.
Their focus can vary-they might be specific to a small part of the text or deal with the entire text. The examiner usually adds incorrect options are designed to trick or confuse students. These options are similarly worded to the statements in the text but they might not be related to that particular question.
Sample Question:
Matching Information
In this question, you will be given a list of options in mixed order and you will have to match each option with a corresponding part of the passage. Unlike the matching headings questions, the answers for this question do not match to the main headings of a paragraph. They can come from anywhere in a paragraph. We have to decide which of these options only fits the sentence grammatically.
A paragraph may match more than once and that does not necessarily mean you have made a mistake.
Matching Features
In this question, you will be given a list of options in mixed order and you will have to match features of two different but somehow connected lists. These features are often a list of options (a job, a name, a location, a city, etc.) or a collection of statements (facts, opinions or even theories).Unlike the matching headings questions, the answers for this question do not match to the main headings of a paragraph. The answers can come from anywhere in a paragraph and they will often be paraphrased in some way or form.
An option may match more than once and that does not necessarily mean you have made a mistake.
Yes/No/Not Given
This question is very similar to true/ false / not given. True/ false / not given always ask for whether or not certain statements agree with the information given in the paragraph. Yes/No/ Not Given questions ask whether or not certain statements agree with the writer’s views and opinions. If a particular view is expressed in the passage, then we answer Yes and if not then we answer No. Not Given refers to information/ opinions that may have only been partially mentioned or not mentioned at all.
All options should be used, so if you have not used an option you have probably made a mistake.
Sample Question:
Diagram Labeling
This question requires you to label a diagram related to the text by using either the corresponding letters to the options or by guessing the correct option. The labels have to be filled using the exact same words as the passage so be careful not paraphrase or misspell a word.
Sample Question: